Before you read about how I almost burned my processor experimenting, you should read about the Precision Boost Overdrive technology. That will help you understand why the temperatures were lower when overclocking with Precision Boost Overdrive and what the result was. If you're not interested, you can skip to the experiment results in the table of contents. But remember: if you try this at home, I am not responsible for the consequences. I did it for myself. And I'm only sharing my experiences with you.
"If one day speed kills me, don't cry. Because I was smiling."
Paul Walker
Theory: Overclocking with Precision Boost Overdrive
Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) is a technology used in modern AMD processors to boost performance beyond standard specifications. This feature enables the processor to achieve higher clock speeds when thermal and electrical conditions allow it. Here's a closer look at how it works:
- Basics: PBO is based on AMD's Precision Boost 2, a technology that dynamically adjusts the processor's clock speed based on available thermal and electrical power as well as system load. Simply put, the better your cooling system, the better results you'll achieve.
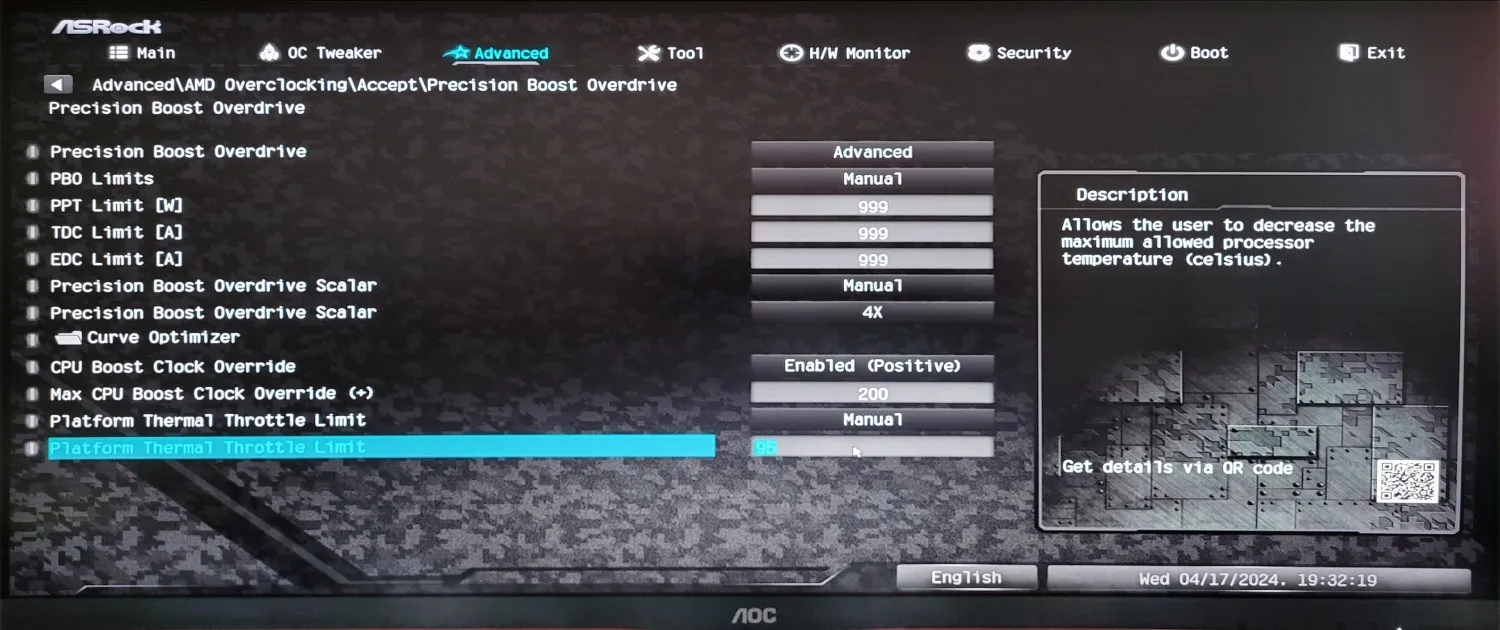
- Limit Expansion: While Precision Boost 2 operates within the processor's safety limits, PBO allows the user to expand these limits. This means you can increase limits for CPU temperature, power delivery, and power consumption to achieve better performance. I am trying to set the temperature limit to 95 degrees so I don't burn the CPU. But you can do whatever you want.
- User Control: PBO gives you the ability to adjust settings in the BIOS or with specialized software. You can decide how aggressively you want to overclock your CPU, depending on your cooling system and other factors.
- Performance Boost: Enabling PBO can lead to a noticeable increase in processor performance, especially in scenarios benefiting from high clock speeds, such as gaming or demanding software.
- Risks and Considerations: It's important to know that exceeding standard processor specifications with PBO can lead to increased wear or a shortened lifespan. Additionally, adequate cooling is necessary to handle the increased temperatures.
By applying PBO, users can increase the performance of their AMD processors beyond the normal limits, but this should be done with caution and considering the potential risks.
In short, if you have a good cooling system, you can increase your processor's performance without damaging it. Everything runs automatically. The system itself adjusts the voltage and frequencies, but within the limit of 95 degrees so the processor doesn't burn out. That's very cool. 20 years ago, I wouldn't have dreamed of this.
Setting up BIOS for overclocking with Precision Boost Overdrive
Let's get started. Before we begin, save the BIOS settings on a USB stick. If something goes wrong, I won't have to waste time restoring default settings. Such as memory frequency, cooler speed, and so on.
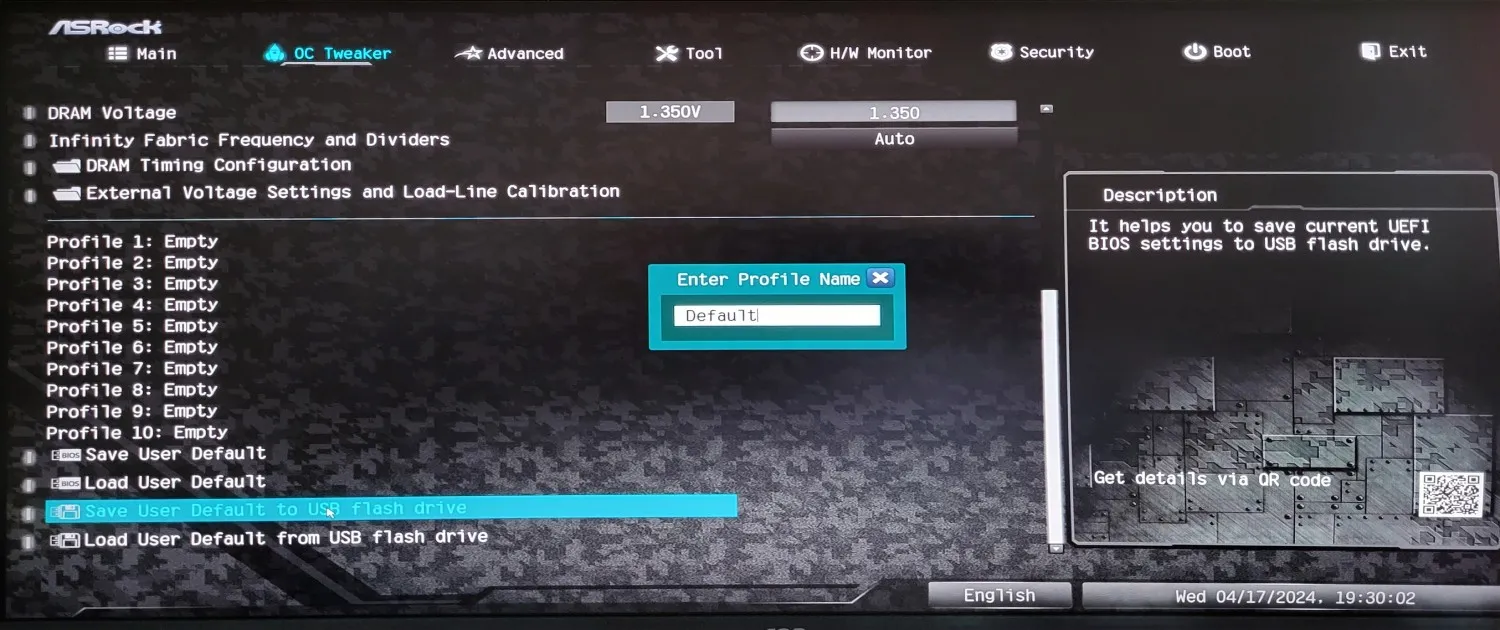
Go to Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) and adjust the parameters as shown in the screenshot. Our goal is to remove all limitations. The outcome depends only on your cooling system, case, and motherboard ventilation.
Press F10 on the keyboard, save the settings, restart, and test.
Theory: Overclocking with Fixed CPU Core Frequency and Voltage
Overclocking Ryzen processors with a fixed frequency and voltage is a popular method to boost performance. Here's a brief introduction to it:
Basic Concept: When overclocking with fixed frequency and voltage, you manually set the clock rate and CPU core voltage instead of using the dynamic adjustments of AMD's Precision Boost. This gives you full control over your processor's performance parameters.
Steps for Overclocking:
- BIOS Access: First, you need to access your system's BIOS. This is typically done by pressing a specific key during startup, such as F2, Del, or Esc.
- Setting Frequency and Voltage: In the BIOS, you can set the CPU core frequency and core voltage. It's advisable to proceed incrementally by increasing the frequency in small steps and adjusting the voltage accordingly to ensure stability.
- Stress Tests: After each adjustment, you should run stress tests to ensure that the processor runs stably under load. Programs like Prime95 or AIDA64 are suitable for this purpose.
- Cooling is Crucial: Since increased frequencies and voltages can lead to higher temperatures, efficient cooling is crucial. Make sure your cooling system, whether air or water, is designed to handle the additional thermal load.
Risks: Manual overclocking can increase the risk of system instabilities, higher wear and tear, and even damage to the processor if not done correctly. Additionally, it may void the processor's warranty.
Benefits: By setting a constant overclock, you can often achieve higher and more consistent performance, especially in demanding applications and games.
To cut a long story short. You will spend a lot of time finding the maximum CPU frequency at which it works. It took me more than two hours for this experiment to find the optimal voltage and frequency settings where the processor survives the ten-minute stress test and does not heat up above 105 degrees. Even though the manufacturer recommends not exceeding 95 degrees.
Driving too fast has never killed anyone, but suddenly stopping...
Jeremy Clarkson
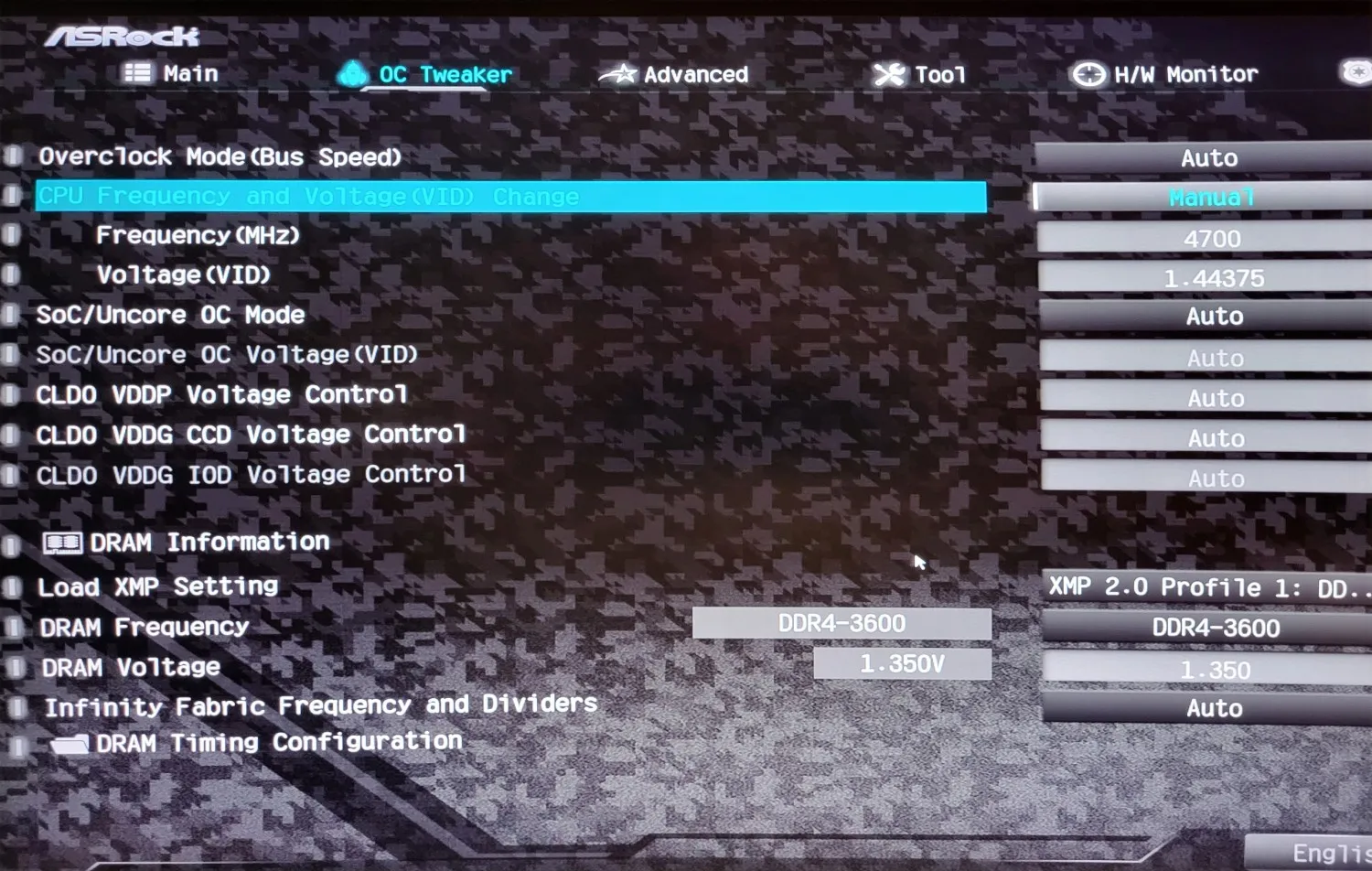
Configure the BIOS for overclocking with fixed CPU speeds and voltages
In fact, I spent two hours changing frequencies and voltages. Here is a screenshot of the successful adjustment.
Test Bench
The test bench is my home computer.
- ASRock B550M Motherboard
- Ryzen 5700X
- 2*16 GB ddr4 3600MHz Cl16
- Arctic 280mm liquid cooling system
- RTX 4060
First, take a look at the results of overclocking with Precision Boost Overdrive.
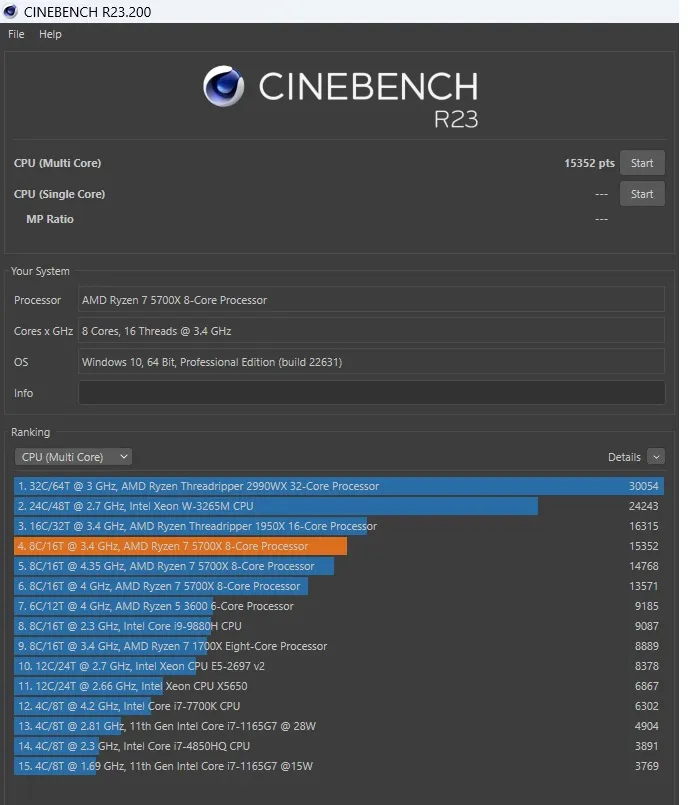
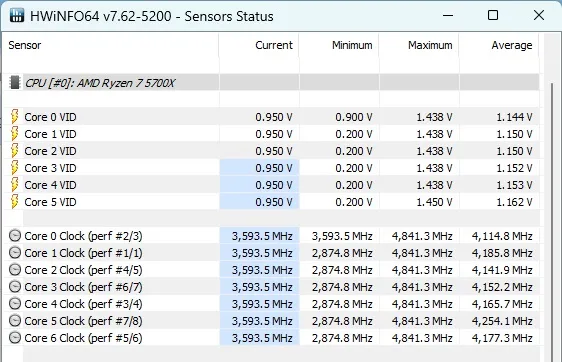
Now the results of overclocking with frequency fixation. Initially, I couldn't pass the test as the system rebooted when starting the test. With a CPU frequency of 4700 MHz, the processor passed the 10-minute stress test. And the result is astonishing.
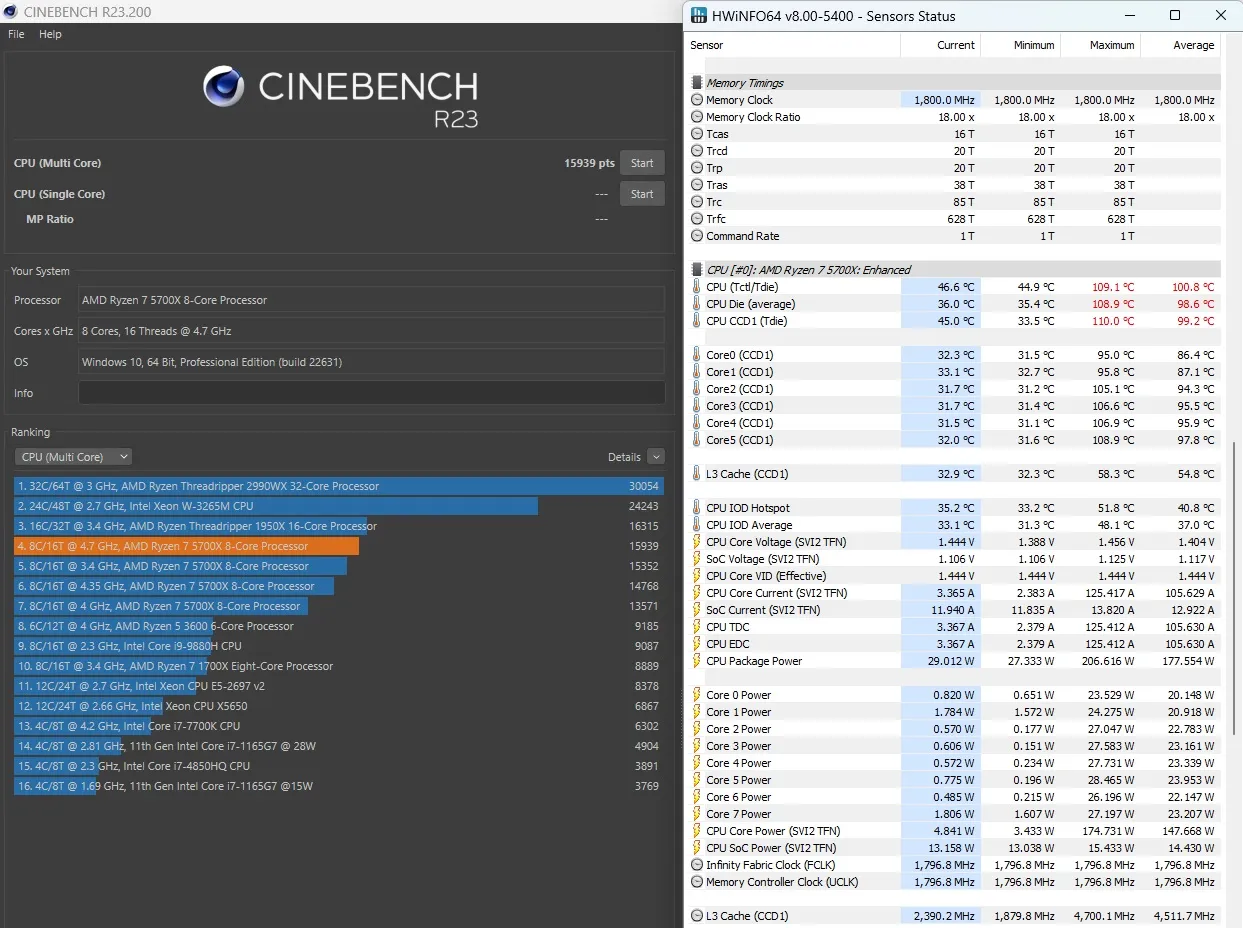
In the Cinebench R23 test, the Ryzen 5700X processor scored 15939 points. That's quite a lot. But the temperature reached 109 degrees. I kept my hand on the pulse to prevent the processor from burning out. But I was eager to complete the test.
Take another look at the screenshot:
- 13571 points - Processor running stock.
- 14768 points - Fixed CPU frequency of 4200 MHz.
- 15352 points - Maximum overclock with Precision Boost Overdrive.
- 15939 points - Maximum overclock with fixed CPU frequency of 5700MHz.
Result: The processor was overclocked by 17.44 percent.
I had fun doing this. But it didn't pay off, of course, because the value of the percentage overclock with 17 percent is too little. Normally, the processor uses 77 watts and provides 13571 points of performance. With the overclock, the processor uses 200 watts and provides only 17 percent more performance.
I have shown you everything I wanted to show you. I wish you all the best, good luck, and successful overclocking!

