A snippet is the classic search result displayed, consisting of a link, title and description and increasingly also with a thumbnail, i.e. a small preview image.
Google is now enriching the SERPs with other types of results from other databases in addition to the ads. This comprehensive mix of results is called Universal Search. This includes in particular
- Images as an image snippet directly in the SERPs and in the dedicated images tab
- Videos as video snippets directly integrated in the SERPs and in their own video tab
- Local search hits directly integrated in the SERPs and in your own Maps tab
- Featured snippets, in which Google often gives a direct answer to the search query (e.g. weather, currency converter etc. or an excerpt from Wikipedia on a question) ... and in this context, AI snippets will soon provide the answers without users even being given the opportunity to click through to the website. BING is already leading the way with the integration of ChatGPT.
- Headlines for current news and events in the SERPs and in your own news tab
- News products
- Jobs
Featured snippets in particular lead to zero-click searches that do not bring any traffic to your website. They are therefore annoying for website operators, especially when Google takes the answer from your own website and presents it directly to the searcher.
Here is an example of a search for "weather today":
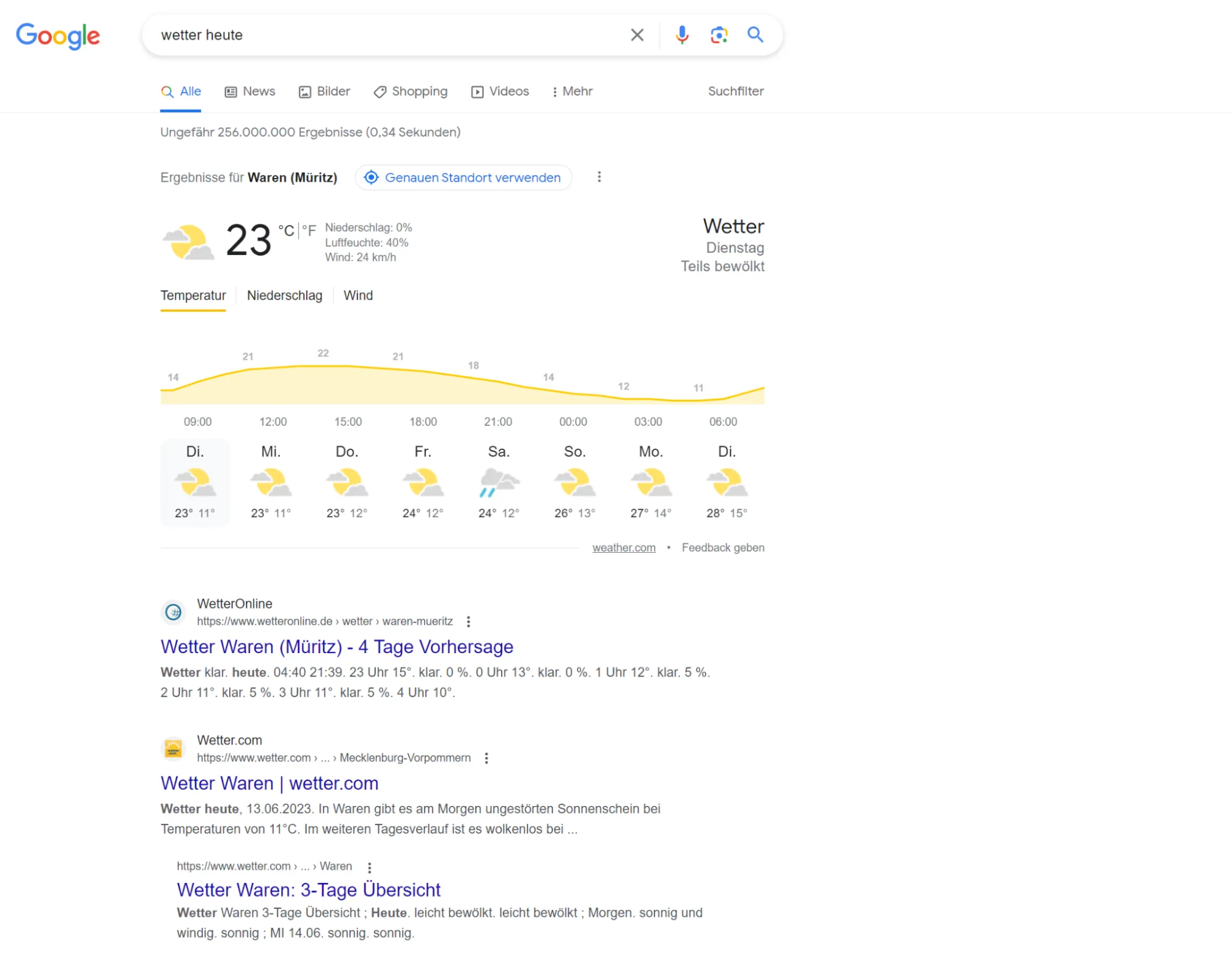
Wetter.com did not put up with this and, as was announced on September 14, 2023, sued Google. The subsidiary of ProSiebenSat.1 Media, Wetter.com, has already confirmed the lawsuit via a spokesperson for the parent company. Wetter.com refers to this as a "particularly serious form of abuse of a dominant market position by Google as a gatekeeper".
For us small marketing managers who can't or don't want to sue Google right away, it only helps to keep an eye on the rankings in Google Search Console or a professional SEO tool and to regularly track visitor numbers via Google Analytics. The textual design of the snippet can also be formulated in such a way that users still click on the associated link because they want to find out more.
All other Universal Search result types - such as jobs or products - offer opportunities to generate more visibility, although these have their own ranking factors and therefore require other optimizations.
It helps to work with structured data to identify the type of content accordingly so that Google has an easy time displaying it in Universal Search (rather your content than that of the competition).
Here you can find basic information from Google about structured data. The complete reference of structured data can be found on schema.org.
An example of how powerful this technique is: When entering the keywords "Pflegekraft Rostock", the MeckCura nursing service appears in Google's jobs widget ahead of its competitors and the major job portals.
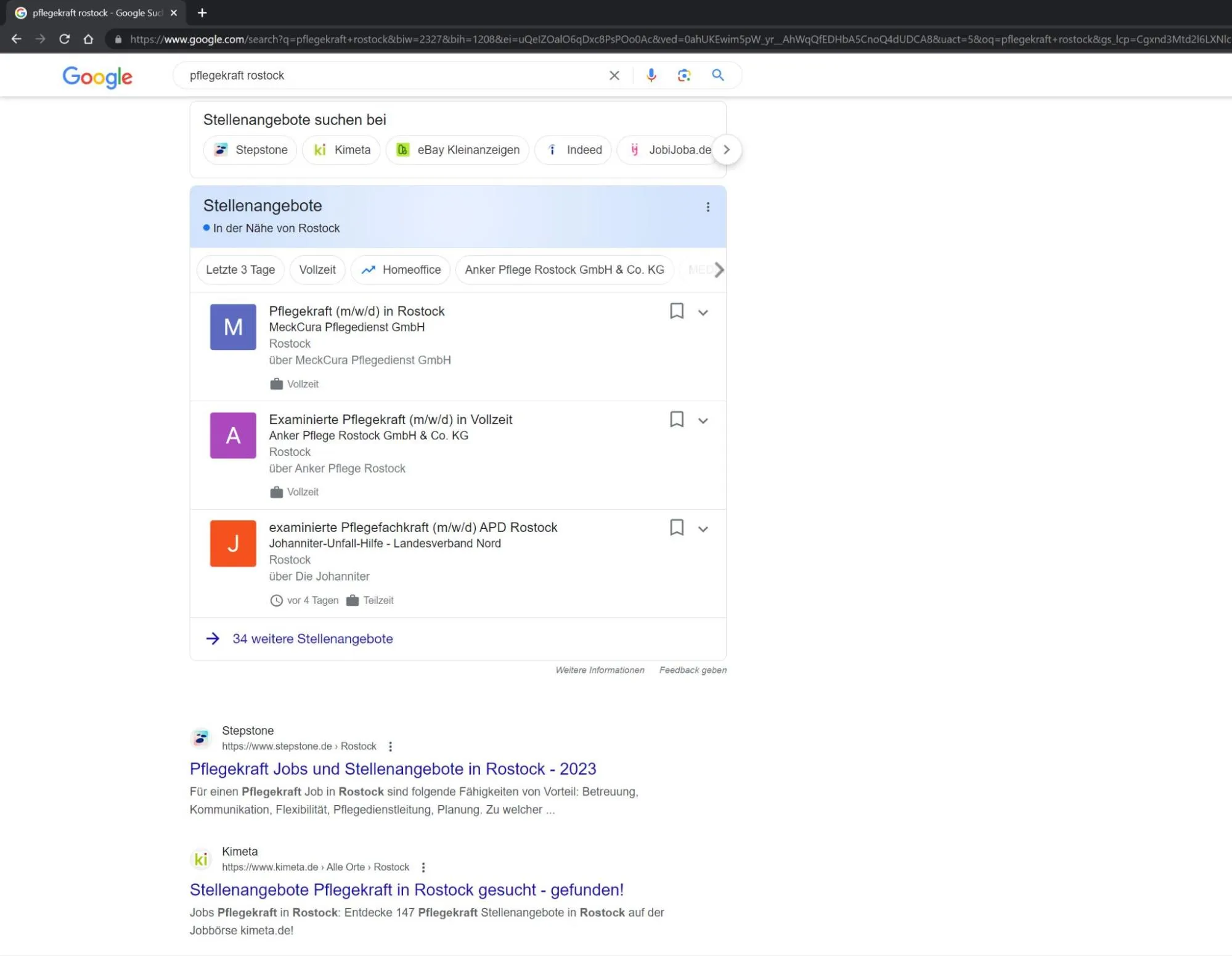
We are particularly pleased about this because MeckCura is a client of our agency and we expanded the job advertisements with structured data a year ago.
The corresponding job advertisement was published here at the time: Careers at MeckCura.
Google even has its own landing page to support companies with job advertisements:
https://jobs.google.com/about/intl/de_ALL/
And here is the help for the structured data:
https://developers.google.com/suche/docs/appearance/structured-data/job-posting?hl=de
It is important to know that the SERPs are constantly changing - depending on how Google classifies and assigns relevance. The layout itself also changes and Google experiments with different result types.


